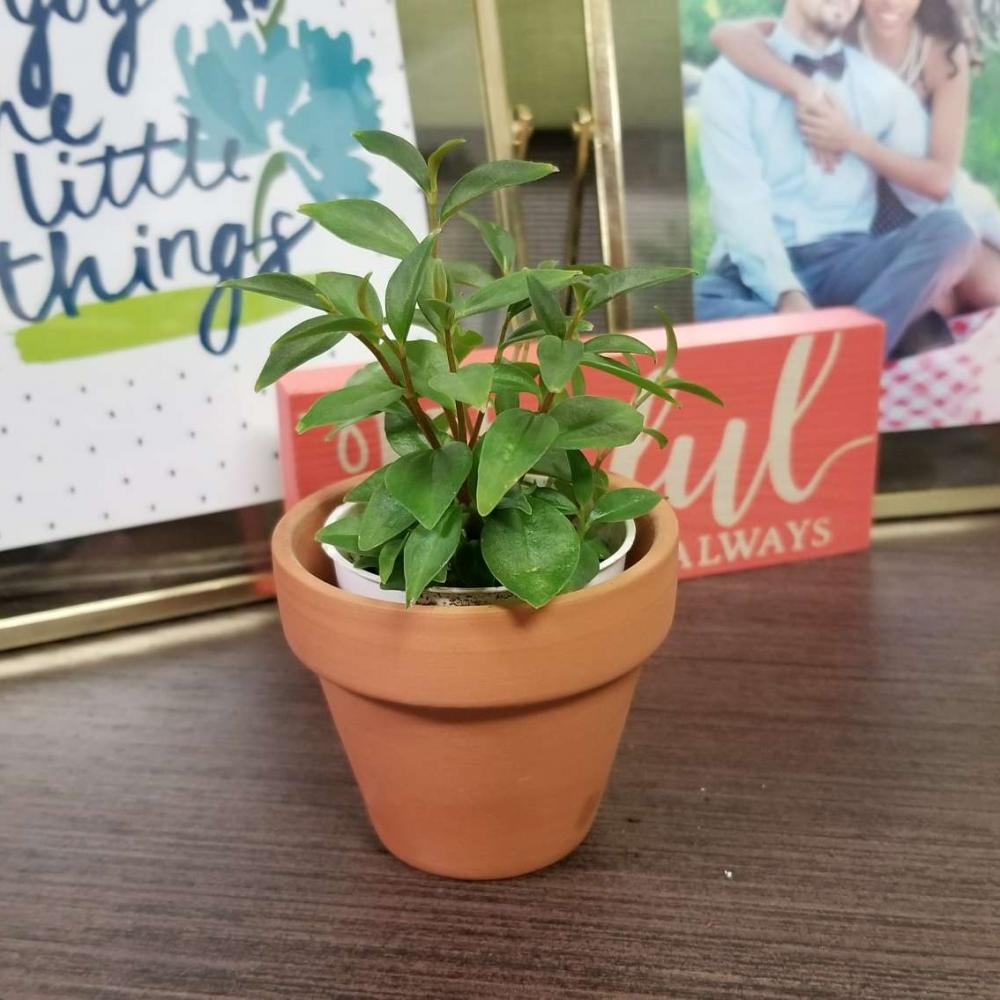
Plant Experience
Detail
LIGHT
Peperomia Houseplants grow well in the bright indirect lightprovided by a west or east-facing window. These plants even grow under fluorescent lights. Insufficient light causes the slow growing peperomia plant to stop growing all together. Direct sunlight burns the leaves.
WATER
Allow the top 50% of the soil to dry out before you water. Over-watering, resulting in root-rot, is the main cause of serious peperomia plant problems. It’s best to water these plants from the bottom. This technique keeps the leaves dry and helps prevent plant diseases. The thick leaves of Peperomia Plants hold water and allow the plant to withstand long periods without moisture.
FERTILIZER
Fertilize peperomia houseplants monthly in the spring and summer with a basic houseplant food at 1/2 the recommended strength. It’s not necessary to feed this plant in the fall and winter.
TEMPERATURE
Warm temperatures between 60-80 F are best. Temperatures below 50-55 F and cold drafts from windows and doors damage peperomia plant leaves.
HUMIDITY
Peperomia plants are originally from the rain forests of Brazil and like a warm humid environment.
FLOWERING
The flowers of peperomia plants are very small and inconsequential. It's the leaves that are so interesting.
PESTS
Houseplant pests such as Mealy Bugs and Aphids can be a problem.
DISEASES
Ringspot, a virus that marks the with unsightly round marks, develops because of the high humidity Peperomia Plants like. Since there is no good treatment for this plant disease, damaged leaves and even the entire infected plant may have to be thrown out. Keep the peperomia leaves dry and provide good air circulation to prevent diseases.
SOIL
Use a well-aerated loose potting soil that drains well.
POT SIZE
: Re-pot peperomia plants to the next size pot when the roots of the plant have filled the existing pot. Planting a peperomia in a pot that is too large prevents the soil from drying out quickly and causes root-rot.
PRUNING
Peperomia plants can be pruned anywhere along the stem. New growth develops from the nodes just below the cut in the stem.
PROPAGATION
Peperomia HousePlants are easily propagated from leaf cuttings, stem tip cuttings, and plant division. Be sure to allow the cut ends of the leaves or stems being used forpropagation to dry out for several hours or overnight before planting them.
Peperomia Houseplants grow well in the bright indirect lightprovided by a west or east-facing window. These plants even grow under fluorescent lights. Insufficient light causes the slow growing peperomia plant to stop growing all together. Direct sunlight burns the leaves.
WATER
Allow the top 50% of the soil to dry out before you water. Over-watering, resulting in root-rot, is the main cause of serious peperomia plant problems. It’s best to water these plants from the bottom. This technique keeps the leaves dry and helps prevent plant diseases. The thick leaves of Peperomia Plants hold water and allow the plant to withstand long periods without moisture.
FERTILIZER
Fertilize peperomia houseplants monthly in the spring and summer with a basic houseplant food at 1/2 the recommended strength. It’s not necessary to feed this plant in the fall and winter.
TEMPERATURE
Warm temperatures between 60-80 F are best. Temperatures below 50-55 F and cold drafts from windows and doors damage peperomia plant leaves.
HUMIDITY
Peperomia plants are originally from the rain forests of Brazil and like a warm humid environment.
FLOWERING
The flowers of peperomia plants are very small and inconsequential. It's the leaves that are so interesting.
PESTS
Houseplant pests such as Mealy Bugs and Aphids can be a problem.
DISEASES
Ringspot, a virus that marks the with unsightly round marks, develops because of the high humidity Peperomia Plants like. Since there is no good treatment for this plant disease, damaged leaves and even the entire infected plant may have to be thrown out. Keep the peperomia leaves dry and provide good air circulation to prevent diseases.
SOIL
Use a well-aerated loose potting soil that drains well.
POT SIZE
: Re-pot peperomia plants to the next size pot when the roots of the plant have filled the existing pot. Planting a peperomia in a pot that is too large prevents the soil from drying out quickly and causes root-rot.
PRUNING
Peperomia plants can be pruned anywhere along the stem. New growth develops from the nodes just below the cut in the stem.
PROPAGATION
Peperomia HousePlants are easily propagated from leaf cuttings, stem tip cuttings, and plant division. Be sure to allow the cut ends of the leaves or stems being used forpropagation to dry out for several hours or overnight before planting them.
Album (1)

brielle
2017-12-06

This is my first growing diary.


Elite Article